
Sevoflurane for Inhalation FDA approval
DescriptionFull Analysis capability
Thin Film Coating Lab
Sevoflurane for Inhalation
Product Details
Indication
Sevoflurane is indicated for the induction and maintenance of general anesthesia for in-hospital and outpatient surgery in adult and pediatric patients.
Clinical pharmacology
Sevoflurane is an inhaled anesthetic used for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia.
Dosage
Sevoflurane should be used by specially calibrated volatilizers to accurately control the concentration of sevoflurane...
Formulation
Inhaler
specification
100ml.
Instruction manual
Approved date October 20, 2008
Revision date December 24, 2008
October 01, 2010 December 1, 2015
Inhalation sevoflurane instructions
Please read the instructions carefully and use them under the guidance of a physician.
【Drug Name】
Generic name: sevoflurane for inhalation
English name: Sevoflurane for Inhalation
Chinese Pinyin: Xiruyong Qifuwan
【Ingredients】The main component of this product is sevoflurane.
Chemical name: 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-(fluoromethoxy)-propane.
Chemical Structure:
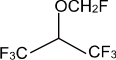
Molecular formula: C4H3F7O Molecular weight: 200.05
This product does not use auxiliary materials.
【Properties】 This product is a colorless clear liquid; it is volatile and non-flammable.
【Indications】 Sevoflurane is indicated for the induction and maintenance of general anesthesia for in-hospital and outpatient surgery in adult and pediatric patients.
【Specification】 100ml.
【Usage and Dosage】 Sevoflurane should be used by a specially calibrated volatilizer to accurately control the concentration of sevoflurane.
The MAC of sevoflurane decreases with age and nitrous oxide. The average MAC for different age groups is as follows:
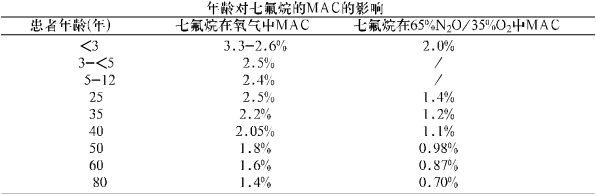
※Pediatric patients use 60% N2O/40% O2
Induction: The dose must be individualized and adjusted according to the patient's age and clinical condition. Barbiturates or other intravenous inducers can be administered immediately after inhalation of sevoflurane. Sevoflurane can be used simultaneously with pure oxygen or oxygen-nitrous oxide to achieve anesthesia induction. Adults, sevoflurane inhalation concentration to 5%, usually can achieve surgical anesthesia within 2 minutes; children, sevoflurane inhalation concentration to 7%, can achieve surgical anesthesia within 2 minutes. As an anesthesia induction in patients who did not take the drug before surgery, the concentration of sevoflurane inhaled was 8%.
Maintenance: The concentration of sevoflurane with or without nitrous oxide to maintain surgical level anesthesia is 0.5% to 3%.
Elderly patients: As with other inhaled anesthetics, surgical anaesthesia is usually maintained at a lower concentration of sevoflurane.
Awakening: The recovery period of sevoflurane anesthesia is usually shorter. Therefore, patients will be asked to reduce surgical pain earlier.
【Adverse reactions】
As with all inhaled anesthetics, sevoflurane can cause dose-related cardiopulmonary dysfunction. The severity of most adverse reactions is mild to moderate and temporary. Nausea and vomiting are the most common after surgery and are similar to the incidence of such reactions with other inhaled anesthetics. These reactions are common sequelae of surgery and general anesthesia, and may be caused by inhaled anesthetics, other medications used during and after surgery, and the patient's response to the surgical procedure.
The following adverse reactions were obtained from clinical trials in more than 3,200 patients in the United States and Europe. The type, severity, and frequency of adverse reactions in patients taking sevoflurane are similar to other inhaled anesthetics.
The most common adverse reactions to sevoflurane were nausea (24%) and vomiting (17%). What is prone to children is anxiety (23%).
Other frequent adverse reactions (≥10%) of sevoflurane are: increased cough and hypotension.
In addition to nausea and vomiting, other frequently occurring adverse reactions (≥10%) are based on age list: adult, hypotension; elderly, hypotension and bradycardia; children, aggravation and cough.
The unfavorable adverse reactions (1% to 10%) of sevoflurane are: excitement, lethargy, chills, bradycardia, dizziness, increased saliva, respiratory disorders, high blood pressure, tachycardia, throat, fever, headache, The body temperature is lowered and the AST is increased.
Adverse reactions (<1%) of sevoflurane accidentally: arrhythmia, increased LDH, elevated ALT, hypoxemia, apnea, leukocytosis, ventricular extrasystole, supraventricular premature contraction, asthma , mental confusion, increased creatinine, urinary retention, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, complete atrioventricular block, dual law, leukopenia.
Very few reports of malignant hyperthermia and acute renal failure.
Postoperative hepatitis is mentioned in a few reports, but there is no definite relationship with sevoflurane.
After the use of sevoflurane, especially in children, there are very few people who will experience convulsions.
Very few reports of pulmonary edema.
As with other anesthetics, some cases report spontaneous sputum and muscle twitching in children induced by sevoflurane anesthesia, but there is no definite relationship with sevoflurane.
The experience of repeated use of sevoflurane is limited. However, there was no significant difference in adverse reactions that occurred for the first time and repeated use.
【taboo】
Sevoflurane is contraindicated in patients known to be allergic to this product; it is contraindicated in patients with known or suspected genetic history of malignant hyperthermia.
【Precautions】
Sevoflurane can only be used by trainers who have received anesthesia. Equipment that maintains airway patency, artificial ventilation, oxygen supply, and recirculation must be prepared for use at any time.
Sevoflurane should be used through specially calibrated special volatilizers to accurately control the concentration of sevoflurane. When the anesthesia is deepened, the blood pressure is too low and the respiratory function is low.
Increasing the concentration of sevoflurane during anesthesia maintenance can result in a dose-dependent decrease in blood pressure. Excessive anesthesia can lead to an excessive decrease in blood pressure, which can be adjusted by lowering the concentration of inhaled sevoflurane. The recovery of general anesthesia should be carefully evaluated before leaving the recovery room.
For some sensitive patients, inhaled anesthetics may induce an acute abnormal increase in skeletal muscle metabolism, increased oxygen demand and cause clinical symptoms of malignant hyperthermia. Therapeutic methods include discontinuation of elicitors (such as sevoflurane), intravenous administration of dantrolene sodium, and conventional supportive therapy. For the possible renal failure in the later stage, the urine volume should be monitored and maintained as much as possible.
For patients with a risk of elevated intracranial pressure, sevoflurane should be used with caution and combined with methods to reduce intracranial pressure, such as hyperventilation. Direct contact of the sevoflurane with the carbon dioxide absorber produces a small amount of Compound A (pentafluoroisopropene fluorocarbon (PIFE)) and a trace amount of Compound B (pentafluoromethoxyisopropene fluoromethane PMFE). The concentration of Compound A increased with the increase of the temperature in the tank and the concentration of the anesthetic; it increased with the decrease of the gas flow rate; the reaction with the strontium silicate was more obvious than the reaction with the sodium sulphate.
Some halogenated anesthetics have been shown to react with dry carbon dioxide absorbers to produce carbon monoxide. To date, there is no evidence that sevoflurane will react like this. However, in order to reduce the risk of carbon monoxide production during the rebreathing cycle and the possibility of an increase in the concentration of carboxyhemoglobin, the carbon dioxide absorbent cannot be dry.
【Pregnant women and lactating women】
There was no other study using sevoflurane in pregnant women (including normal delivery) except for a caesarean section study involving only a small number of patients.
Pregnant rats only cause a decrease in their fetal weight and an increase in bone turnover at concentrations of poisoning. No adverse effects on the fetus were found in the rabbit experiment.
Therefore, sevoflurane can be used only when it is clearly needed during pregnancy.
It is not clear whether sevoflurane will be secreted with breast milk, so lactating women should be used with caution.
【Children's medication】
The concentration of anesthesia maintenance using this product is age-dependent. When used in combination with nitrous oxide, the MAC dose in children should be reduced. The MAC value of this product for premature babies was not determined.
Epilepsy may be induced after inhalation of this product, most of which occur in patients over 2 months, and most of them do not have risk factors for susceptibility. Children with a risk of epilepsy need to be clinically identified.
【Geriatric Use】As with other inhaled anesthetics, usually a lower concentration of sevoflurane can maintain surgical anesthesia in elderly patients.
【medicine interactions】
Sevoflurane significantly enhances the muscle relaxant effect of non-depolarizing muscle relaxants. Therefore, when sevoflurane is used, the dose of these drugs should be appropriately adjusted.
Sevoflurane is similar to isoflurane in that it requires the addition of epinephrine when an exogenous arrhythmia occurs due to myocardial sensitivity.
The MAC of sevoflurane decreases with increasing nitrous oxide, see Table 'The effect of age on the MAC of sevoflurane' (see usage).
Similar to other drugs, sevoflurane can be used in combination with intravenous anesthetics such as propofol to reduce its concentration.
CYP2E1 inducers (such as isoniazid, alcohol) increase the metabolism of sevoflurane, but barbiturates do not increase their metabolism.
【Drug overdose】 should be stopped immediately after the excess of sevoflurane, keep the trachea unobstructed, inhale pure oxygen to help or control breathing, and maintain cardiovascular function.
【Pharmacology and Toxicology】
Pharmacological action
Sevoflurane is an inhaled anesthetic used for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia.
Toxicological research
Genotoxicity: This product has no mutagenic effect in Ames test, mouse micronucleus test, mouse lymphoma mutagenesis test, human lymphocyte culture test, mammalian cell transformation test and 32P DNA addition test in mammals. No chromosomal abnormalities were caused in the cell test.
Reproductive toxicity: Rat and rabbit test results showed that sevoflurane had no significant damage to animal fertility and embryos at the minimum non-toxic dose of 0.3 MAC (minimum alveolar concentration). Pregnant rats only cause a decrease in their fetal weight and an increase in bone turnover at concentrations of poisoning. No adverse effects on the fetus were found in the rabbit experiment. This product is rapidly excreted in the body, and the drug in the milk 24 hours after anesthesia has no clinical significance.
【Pharmacokinetics】
The lower solubility of sevoflurane in the blood causes its alveolar drug concentration to rise rapidly during anesthesia induction and then rapidly decline after stopping inhalation.
Less than 5% of the sevoflurane in the human body is absorbed and metabolized. Sevoflurane is rapidly and extensively cleared by the lungs, reducing its metabolizable amount. Sevoflurane is defluorinated by cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2E1 to produce hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP), while releasing inorganic fluoride and carbon dioxide (or single carbon fragments). HFIP is rapidly converted to glucuronic acid and excreted with urine.
Known CYP2E1 inducers (such as isoniazid, alcohol) increase the metabolism of sevoflurane, but barbiturates do not increase their metabolism.
There is a transient increase in the level of inorganic fluoride in the plasma during sevoflurane anesthesia and after anesthesia. Typically, the concentration of inorganic fluoride will peak within 2 hours of sevoflurane anesthesia and return to pre-operative levels within 48 hours.
【Storage】shading, sealed, and stored in a cool place (not more than 20 ° C).
【Packaging】 medicinal glass bottles. 1 bottle / box.
【Validity period】 24 months.
【Executive Standards】 "Chinese Pharmacopoeia" 2015 Edition 2
【Approval No.】 National Drug Standard H20080681
【manufacturer】
Company Name: Lunan Beite Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Address: No. 243, Yinqueshan Road, Linyi City, Shandong Province
Postal code: 276006
Phone number: (0539) 8336336 (Sales) 8336337 (Quality Management Department)
Fax number: (0539) 8336029 (Sales) 8336338 (Quality Management Department)
Website: www.LUNAN.com.cn
24-hour customer service hotline: 400-0539-310
