Epirubicin Hydrochloride for Injection
DescriptionFull Analysis capability
Thin Film Coating Lab
Epirubicin Hydrochloride for Injection
Indication
Treatment of malignant lymphoma, breast cancer, lung cancer, soft tissue sarcoma, esophageal cancer, gastric cancer, liver cancer, pancreatic cancer, melanoma, colorectal cancer, ovarian cancer, multiple myeloma, leukemia. Intravesical administration contributes to the treatment of superficial bladder cancer, carcinoma in situ and prevention of recurrence after transurethral resection.
Clinical pharmacology
Epirubicin is an anthracycline cytotoxic drug. Although anthracyclines are known to interfere with many biochemical and biological functions in eukaryotic cells, the precise mechanism of cytotoxicity and/or anti-cell proliferation of epirubicin has not been fully elucidated. The planar ring of epirubicin is embedded between the base pairs to bind to the DNA to form a complex, which in turn inhibits the synthesis of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and proteins. This insertion process also triggers topoisomerase II to cleave DNA, producing a cytocidal effect. Epirubicin also inhibits DNA-cleaving enzyme activity, prevents enzyme-induced DNA double-strand melting, and interferes with replication and transcription. Epirubicin can also participate in the oxidation/reduction reaction by producing cytotoxic free radicals. The anti-cell proliferation and cytotoxic effects of epirubicin stem from these or other possible mechanisms of action. Epirubicin has an in vitro cytotoxic effect on a variety of established primary cultures of murine, human cell lines and human tumors. At the same time, it also has an in vivo anti-tumor effect on human cancer xenografts (including breast cancer) in murine tumors and athymic mice.
Dosage
Dosage according to the disease, please follow the doctor's advice. (see instructions for details)
Formulation
Powder needle
specification
10mg
Instruction manual
Approval date: August 16, 2012
Revision date: December 1, 2015
Epirubicin hydrochloride injection instructions
Please read the instructions carefully and use them under the guidance of a physician.
Warning: tissue necrosis, secondary acute leukemia and myelosuppression
1. If extravasation occurs during administration, it can cause severe local tissue necrosis. Do not be administered via the muscle or subcutaneous route.
2. Cardiotoxicity may occur during treatment with epirubicin or months or even years after treatment, including fatal congestive heart failure (CHF), with a clinically significant CHF probability of approximately 0.9 at a cumulative dose of 550 mg/m2. %, 1.6% at a cumulative dose of 700 mg/m2 and 3.3% at a cumulative dose of 900 mg/m2. In the clinical trial of adjuvant therapy for breast cancer, the maximum cumulative dose was 720 mg/m2. The risk of CHF increases rapidly when the cumulative dose exceeds 900 mg/m2, so extreme caution must be used if it exceeds this dose. Active or inactive heart disease, previous or current radiotherapy with mediastinal/pericardial area, previous anthracycline or steroid therapy, or increased risk of cardiotoxicity in patients with other cardiotoxic drugs . Cardiotoxicity of epirubicin may also occur at lower cumulative doses or without risk factors for heart risk.
3. Secondary acute myeloid leukemia (AML) has been reported in breast cancer patients treated with anthracyclines including epirubicin. When such drugs are combined with anti-tumor drugs that destroy DNA, especially in patients who have received high-intensity cytotoxic drugs, or higher doses of anthracyclines, refractory secondary leukemia occurs. It may be more common. The probability of treatment-related AML or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) in 7110 breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant therapy with epirubicin was 0.27% in 3 years, 0.46% in 5 years, and 0.55% in 8 years.
4. Serious bone marrow suppression may have occurred.
【Drug Name】
Generic name: epirubicin hydrochloride for injection
English name: Epirubicin Hydrochloride for Injection
Pinyin: Zhusheyong Yansuan Biaoroubixing
【ingredients】
The main component of this product is epirubicin hydrochloride.
Chemical name: (8S, 10S)-10-[(3-Amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L-arabinopyranosyl)oxy]-6,8,11-trihydroxy-8- (hydroxyacetyl)-1-methoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrotetracene-5,12-dione hydrochloride
Chemical Structure:
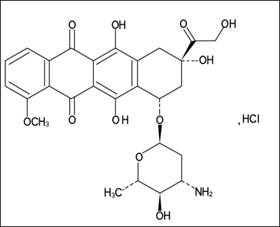
Molecular formula: C27H29NO11·HCl
Molecular weight: 579.98
Excipients: lactose, methyl paraben.
【Properties】 This product is red or orange-red loose mass or powder, which is hygroscopic.
【indications】
Treatment of malignant lymphoma, breast cancer, lung cancer, soft tissue sarcoma, esophageal cancer, gastric cancer, liver cancer, pancreatic cancer, melanoma, colorectal cancer, ovarian cancer, multiple myeloma, leukemia.
Intravesical administration contributes to the treatment of superficial bladder cancer, carcinoma in situ and prevention of recurrence after transurethral resection.
【Specification】10mg
【Dosage】
Routine dose: When epirubicin is administered alone, the adult dose is 60-120 mg/m2 per body surface area. When epirubicin is used to adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer patients with subgingival lymphoid positive, the recommended starting dose For intravenous injection of 100-120 mg/m2, the total starting dose for each course of treatment can be administered alone or in divided doses for 2-3 consecutive days. According to the patient's blood image can be reused 21 days apart.
Optimized dose: High doses can be used to treat lung and breast cancer. When administered alone, the recommended starting dose for adults is up to 135 mg/m2 per body surface area, once on the first day of each course of treatment or on the first, second, and third days of each course of treatment, 3- Once every 4 weeks. In combination with chemotherapy, the recommended starting dose is up to 120 mg/m2 based on body surface area, administered on the first day of each course of treatment, once every 3-4 weeks. Administered intravenously. According to the patient's blood image can be reused 21 days apart.
Intravesical administration: Epirubicin is perfused with a catheter and should remain in the bladder for an hour or so. During perfusion, the patient should change position frequently to ensure maximum contact with the drug in the bladder mucosa. In order to avoid improper dilution of the drug by the urine, patients should be advised not to drink any liquid 12 hours before perfusion. The doctor should instruct the patient to empty the urine at the end of treatment.
For superficial bladder cancer, epirubicin 50 mg is dissolved in 25 to 50 mL of normal saline once a week for 8 times. For cases with local toxicity (chemical cystitis), each dose can be reduced to 30 mg. The patient also received 50 mg of the same dose of the drug once a week for 4 times, then 11 times a month. The doctor can adjust the number of doses according to the patient's condition.
【Adverse reactions】
1. Similar to doxorubicin, but to a lesser extent, especially cardiotoxicity and myelosuppressive toxicity;
2, other adverse reactions are: hair loss, 60-90% of cases can occur, generally reversible, males have a beard growth inhibition; mucositis, the first 5-10 days of medication, usually occurs in the lingual and sublingual mucosa; Gastrointestinal dysfunction, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea; occasional fever, chills, urticaria, hyperpigmentation, joint pain.
【taboo】
1. It is contraindicated in patients who have obvious myelosuppression due to chemotherapy or radiotherapy;
2. Patients who have used large doses of anthracyclines (such as doxorubicin or daunorubicin) are banned;
3. Disabled patients with recent or previous history of cardiac damage;
4. Disabled intravesical instillation in patients with hematuria.
【Precautions】
1. About cardiotoxicity
(1) can cause myocardial damage, heart failure. Animal tests and short-term human trials have shown that epirubicin is less cardiotoxic than its isomer, doxorubicin. Comparative studies have shown that the ratio of epirubicin and doxorubicin to the same degree of cardiac dysfunction is 2:1. Cardiac function should still be closely monitored during the treatment of epirubicin to reduce the risk of heart failure (this heart failure can even occur a few weeks after termination of treatment and may not be effective for the corresponding medication);
(2) The potential risk of epirubicin cardiotoxicity may increase in patients with current or previous mediastinal and pericardial radiotherapy;
(3) Care should be taken when combining with any potentially cardiotoxic drug in determining the maximum cumulative dose of epirubicin;
(4) An electrocardiogram should be performed before and after each course of treatment. Anthracyclines, especially doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy, exhibit persistent low voltage on the electrocardiogram of the QRS complex, prolonged contraction interval beyond the normal range (PEP/LVET), and reduced ejection fraction. For patients receiving epirubicin, ECG monitoring is very important, and cardiac function can be assessed by non-invasive techniques such as electrocardiography and echocardiography. The ejection fraction can be measured by radionuclide angiography if necessary.
(5) When the total cumulative dose of epirubicin exceeds 900 mg/m2, the incidence of progressive congestive heart failure (CHF) is significantly increased, and the use of this cumulative dose needs to be very careful. When the total cumulative dose of epirubicin exceeds 900 mg/m2, there is a risk of causing primary cardiomyopathy, and the use of this cumulative dose needs to be very careful. Risk factors for developing cardiotoxicity include active or inactive cardiovascular disease, current or previous radiotherapy in the mediastinum/peripheral region, previous use of other anthracyclines or anthraquinone drugs, and concurrent use of other inhibitory myocardium A systolic drug or a cardiotoxic drug (such as trastuzumab). Unless the patient's heart function is closely monitored, anthracyclines, including epirubicin, cannot be used concurrently with other cardiotoxic drugs. Patients receiving anthracyclines after discontinuing use of other cardiotoxic drugs (especially drugs with long half-lives such as trastuzumab) may also increase the risk of developing cardiotoxicity. The half-life of trastuzumab is 28.5 days and can last up to 24 weeks in the blood circulation. Therefore, if possible, physicians should avoid anthracycline-based treatment within 24 weeks of discontinuation of trastuzumab. If an anthracycline antibiotic is needed before the event. Care must be taken to detect heart function.
2, on the impact of liver and kidney function
(1) Since epirubicin is excreted by the liver system, liver dysfunction should be reduced to avoid accumulation of poisoning. Patients with moderate liver function impairment (bilirubin 1.4-3mg/100ml or BSP retention 9-15%), the dose should be reduced by 50%. Patients with severe liver function impairment (bilirubin greater than 3mg/100ml or BSP retention greater than 15%), the dose should be reduced by 75%;
(2) Patients with moderate renal impairment do not need to reduce the dose because only a small amount of the drug is excreted through the kidneys. Epirubicin, like other cytotoxic drugs, causes hyperuricemia due to rapid disintegration of tumor cells. Blood uric acid level should be checked, and this phenomenon should be controlled by drugs; in addition, urine red staining may occur within 1-2 days of administration;
3, on bone marrow suppression
It can cause white blood cells and thrombocytopenia, and hematological monitoring should be performed regularly.
4, about the instructions for administration
(1) intravenous administration, diluted with saline or water for injection, so that the final concentration does not exceed 2mg / ml;
(2) It is recommended to inject normal saline to check the patency of the infusion tube and the injection needle is indeed after the vein, and then administered through the unobstructed infusion tube. In order to reduce the risk of drug spillage and to ensure that the vein is rinsed with saline after administration;
(3) Overflow of veins during epirubicin injection can cause serious damage or even necrosis of the tissue. Small vein injections or repeated injections of the same blood vessel can cause venous sclerosis. It is recommended to have a good central vein infusion;
(4) No intramuscular and intrathecal injection.
5, secondary leukemia
It has been reported that patients with anthracyclines (including epirubicin) develop secondary leukemia with or without pre-leukemia symptoms. Secondary leukemia is more common in the following situations: when combined with an anticancer drug whose mechanism of action is to destroy the DNA structure; or when the patient has previously used cytotoxic drugs; or when the anthracycline treatment dose is increased. The incubation period for such leukemias is generally 1-3 years.
6. Impact on the reproductive system
Epirubicin can destroy sperm chromosomes, and male patients undergoing treatment with epirubicin should adopt effective methods of contraception. Epirubicin may cause premenopausal women with amenorrhea or premenopausal.
7, immunosuppressive effect / increase susceptibility to infection
Inhalation of live or live attenuated vaccines for patients receiving chemotherapy drugs, including epirubicin, resulting in immunocompromised, may result in serious or even fatal infections. Patients receiving epirubicin should avoid live vaccines. Dead or inactivated vaccines can be vaccinated, but the immune response to these vaccines may be reduced.
【Pregnant women and lactating women】
There is no definitive data on whether epirubicin has an adverse effect on human fertility and whether it has teratogenic or other harmful effects on the fetus. However, there are experimental data suggesting that epirubicin is similar to most antitumor drugs and immunosuppressive agents, and exhibits mutagenicity and carcinogenicity in animals under specific test conditions. Can reduce the survival rate of the fetus. Therefore, this product is not recommended during pregnancy, and lactating women are prohibited.
【Children's medication】 There are no special requirements for children's medication.
【Geriatric medication】 elderly patients with cardiac dysfunction should be used with caution or reduced.
【medicine interactions】
1, epirubicin can be combined with other anti-tumor drugs, but the amount of epirubicin should be reduced. Do not use in the same syringe when used in combination.
2, epirubicin can not be mixed with heparin injection, because the chemical nature of the two is not compatible, precipitation will occur at a certain concentration.
3. Epirubicin is mainly metabolized in the liver. Any drug that causes liver function changes during treatment will affect the metabolism, pharmacokinetics, efficacy and/or toxicity of epirubicin.
4. The use of paclitaxel before the administration of epirubicin causes an increase in the prodrug and metabolite blood levels of epirubicin, in which the metabolite is neither active nor toxic. When paclitaxel or docetaxel was administered in combination with epirubicin, there was no effect on the pharmacokinetics of epirubicin.
【Drug overdose】
The total limit of this product is 550-800mg/m2 body surface area. 9411 patients treated with epirubicin, most of them are patients with advanced solid tumors. When the cumulative dose reaches 550mg/m2, clinically obvious congestive heart failure occurs. The patient was approximately 0.9%; approximately 1.6% when the cumulative dose reached 700 mg/m2; and approximately 3.3% when the cumulative dose reached 900 mg/m2. The use of epirubicin in the adjuvant treatment of breast cancer has a maximum cumulative dose of 720 mg/m2 in clinical trials.
There are no known antidote to epirubicin. A 36-year-old male patient with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma received epirubicin 95 mg/m2 once daily for 5 consecutive days. After 5 days, he developed bone marrow growth, grade 4 mucositis, and gastrointestinal tract. Bleeding. No acute cardiotoxicity was observed. He received complete recovery after treatment with antibiotics, colony stimulating factors and antifungal drugs. A 63-year-old female patient with liver metastases from breast cancer received a single dose of epirubicin 320 mg/m2. She was hospitalized for hyperthermia and multiple organ failure with lactic acidosis and lactate dehydrogenase. He died 24 hours after taking epirubicin. There are other cases where the recommended dose is exceeded, with doses ranging from 150 to 250 mg/m2. The adverse events observed in these cases were similar to the known toxicity of epirubicin. Most patients recover after giving appropriate supportive care.
If overdose occurs, supportive care (including antibiotic therapy, transfusion or platelet transfusion, colony stimulating factor and close monitoring) should be provided until toxicity is restored. Delayed CHF may occur several months after anthracycline administration, and CHF symptoms should be continuously observed and appropriate supportive care should be given.
【Pharmacology and Toxicology】
Pharmacological action
Epirubicin is an anthracycline cytotoxic drug. Although anthracyclines are known to interfere with many biochemical and biological functions in eukaryotic cells, the precise mechanism of cytotoxicity and/or anti-cell proliferation of epirubicin has not been fully elucidated.
The planar ring of epirubicin is embedded between the base pairs to bind to the DNA to form a complex, which in turn inhibits the synthesis of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and proteins. This insertion process also triggers topoisomerase II to cleave DNA, producing a cytocidal effect. Epirubicin also inhibits DNA-cleaving enzyme activity, prevents enzyme-induced DNA double-strand melting, and interferes with replication and transcription. Epirubicin can also participate in the oxidation/reduction reaction by producing cytotoxic free radicals. The anti-cell proliferation and cytotoxic effects of epirubicin stem from these or other possible mechanisms of action.
Epirubicin has an in vitro cytotoxic effect on a variety of established primary cultures of murine, human cell lines and human tumors. At the same time, it also has anti-tumor effects in vivo in murine and athymic mouse human cancer xenografts, including breast cancer.
Toxicological research
Genotoxicity
The results of Ames test showed that epirubicin could cause bacterial mutation regardless of metabolic activation; HGPRT test was performed on V79 Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts, and there was mutagenic effect in the absence of metabolic activation. There was no mutagenic effect under the conditions of activation; in the chromosome aberration test of human lymphocytes, epirubicin showed mutagenic effects regardless of metabolic activation. In vivo experiments in mouse bone marrow chromosomal aberrations, epirubicin also showed mutagenic effects.
Reproductive toxicity
In the rat fertility test, male rats were given epirubicin daily for 9 weeks, and then mated with female rats (the female rats were administered daily from 2 weeks before mating, and continued to be administered until the 7th day of pregnancy). Rats were infertile when the dose of rats of both sexes was 0.3 mg/kg/day (about 0.015 times the body surface area, about 0.015 times the maximum recommended single dose). The 0.1 mg/kg/day group had no effect on mating behavior or fertility in rats, but it caused atrophy of testis and epididymis in male rats and decreased sperm production. The 0.1 mg/kg/day group also causes embryo death. The 0.03 mg/kg/day group (in terms of body surface area, approximately 0.0015 times the single recommended dose for the maximum recommended person) increased the incidence of embryonic developmental delay. Administration of epirubicin in rabbits and dogs also causes atrophy of male reproductive organs. A single intravenous injection of epirubicin 20.5, 12 mg/kg in mice and rats (about 0.5 times the maximum recommended human dose in terms of body surface area) resulted in testicular atrophy. A single dose of epirubicin at 16.7 mg/kg resulted in atrophy of the rat uterus.
Carcinogenicity
A routine long-term animal test has not been performed to evaluate the potential carcinogenic effect of epirubicin, but female rats received a single intravenous injection of epirubicin 3.6 mg/kg (in terms of body surface area, approximately 0.2 times the maximum recommended human dose) One year after administration, the incidence of breast cancer (mainly fibroadenomas) is approximately doubled. Rats were given an intravenous injection of epirubicin 0.5 mg/kg every 3 weeks (approximately 0.025 times the maximum recommended human dose, based on body surface area) for a total of 10 doses. Under the 18-month observation period, male rats were subcutaneously The incidence of fibroids is increased. In addition, the born rat is injected subcutaneously with epirubicin 0.75 or 1.0 mg/kg/day on the first day or the 10th day after birth (in terms of human body surface area, about 0.015 times the maximum recommended human dose). A total of 8 doses were administered, and the tumor incidence rate was higher than that of the control group during the observation period in 24 months.
【Pharmacokinetics】
Metabolism and excretion in the body are more rapid than the stars, the average plasma half-life of about 40 hours, mainly in the liver metabolism, excreted by the bile. Within 48 hours, 9-10% of the dose was excreted by the urine, and within 4 days, 40% of the dose was administered by the bile, which did not pass the blood-brain barrier. For patients with liver metastases and impaired liver function, the concentration of the drug in plasma is maintained for a longer period of time, so the dose should be appropriately reduced. Normal renal function has little effect on the pharmacokinetic properties of this product.
【Storage】shading, sealed, and stored in a cool place (not more than 20 ° C).
【Package】 vial, bromobutyl rubber stopper. 1 bottle / box.
【Validity Period】24 months
【Executive Standards】 "Chinese Pharmacopoeia" 2015 Edition 2
【Approval No.】National Drug Standard H20123260
【manufacturer】
Company Name: Shandong New Times Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Address: No. 1, North Outer Ring Road, Feixian County, Shandong Province
Postal code: 273400
Phone number: 0539-8336336 (Sales) 5030608 (Quality Management Department)
Fax number: 0539-5030900
Website: www.LUNAN.com.cn
24-hour customer service hotline: 400-0539-310
